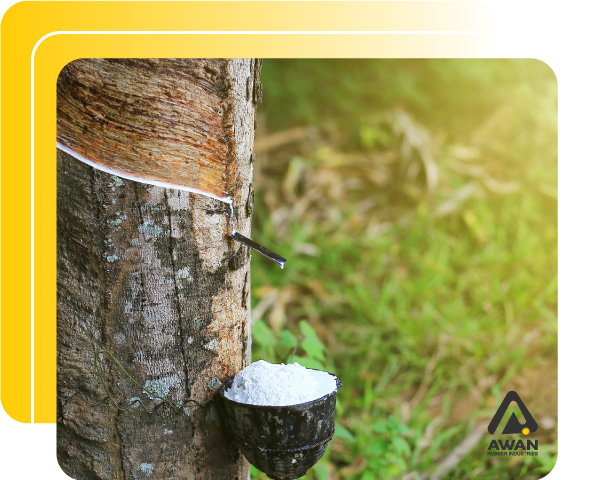

Natural Rubber
Natural rubber—also known as India or gum rubber—is derived from the milky liquid (i.e., latex) present in the Heave brasiliensis tree. Some of the material’s key characteristics are high tear and tensile strength, resilience, and resistance to abrasion, friction, extreme temperatures, and water swell. Typical uses include adhesives, flooring and roofing, gloves, insulation, and tires.
Neoprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber—also called chloroprene—is one of the oldest types of synthetic rubber. Compared with natural rubber and other synthetic rubbers, it exhibits an exceptionally low susceptibility to burning, corrosion, and degradation. This quality makes it the perfect base material for adhesives and corrosion resistant coatings. Its ability to maintain good mechanical properties over a wide temperature range also suits it for use in high-pressure gaskets, belts, and window and door seals.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber—also referred to as polysiloxane—is known for its malleability, biocompatibility, and resistance to extreme temperatures, fire, ozone, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. It is available in both solid and liquid forms in a variety of colors. Its chemically inert nature makes it ideal for use in parts and products that demand biocompatibility (such as gloves, respiratory masks, implants, and other medical products) and chemical resistance (such as baby care items, cosmetic applicators, and food containers and instruments).
Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber—also known as Buna-N rubber or nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR)—demonstrates several desirable mechanical and chemical properties, such as resistance to compression set, heat, oil and gas, and wear. These traits make it suitable for use in automotive gaskets and seals, O-rings, and engine hoses. It is also used in medical products (e.g., surgical gloves) since it lacks the allergenic proteins of latex-based rubbers and maintains its structural integrity better than silicone rubber.
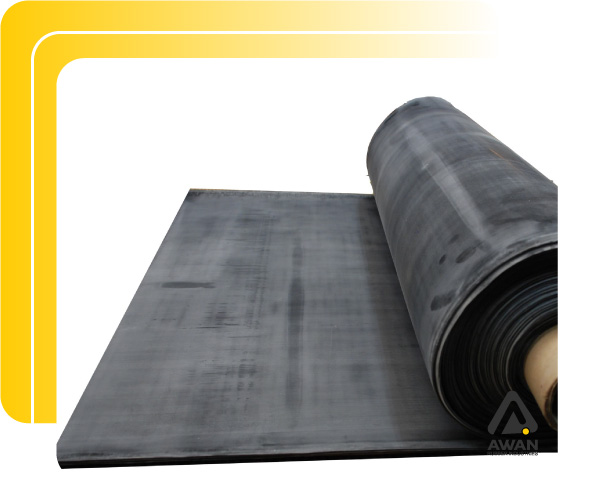

EPDM Rubber
Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is a synthetic rubber that exhibits excellent durability, resisting damage and degradation from extreme temperatures and weather conditions. These qualities make it suitable for use in outdoor parts and products, such as roofing sealants, hoses, and seals. Its superior noise and thermal insulation properties also suit it for use in automobile systems.
Fluor silicone Rubber
Fluor silicone rubber—also called FVMQ—is highly resistant to extreme temperatures (-100–350 degrees Fahrenheit), transmission fluids, petroleum oils and fuels, synthetic lubricants, fire, and ozone. These properties make it an ideal material for aircraft fuel systems and other highly specialized industrial applications
